Recovered Carbon Black and Its Market Potential
Recovered carbon black (rCB) is fast becoming a critical material in the shift toward sustainable manufacturing, offering a scalable alternative to virgin carbon black with growing demand across multiple industries. Despite recent technological advances and the gradual development of circular economy concepts, markets for tire pyrolysis products can still be regarded as nascent. In this article, we introduce what carbon black is, elaborate on the fields of application of virgin carbon black, and attempt to estimate the potential of recovered carbon black to replace its environmentally harmful counterpart – virgin material.
At the end of this article, we estimate the potential annual market size of recovered carbon black, assuming a modest virgin carbon black substitution rate of 20%. The numbers suggest that recovered carbon black production is a profitable business with numerous opportunities for growth.
Carbon black: Introduction and definitions
Traditionally, Carbon Black (CB) has been used as both a reinforcing agent and filler in automobile tires. Along with a better understanding of CB’s unique properties as a material, it is presently used in a much wider range of applications across a large variety of products – car tires, conveyor belts, inks, plastic pipes, rubber mats, shoe soles, and so forth. Virgin CB contains only trace amounts of impurities, and carbon content is very close to 100%.
Virgin Carbon Black (vCB) is a material in the form of fine black powder produced through the incomplete combustion of heavy petroleum products, such as FCC tar, coal tar, or ethylene cracking tar. Carbon black is a form of paracrystalline carbon that has a high surface-area-to-volume ratio, albeit lower than that of activated carbon. The highest volume use of carbon black is as a reinforcing filler in rubber products, especially tires. While a pure gum vulcanization of styrene-butadiene has a tensile strength of no more than 2 MPa and negligible abrasion resistance, compounding it with 50% carbon black by weight improves its tensile strength and wear resistance.
Carbon Char (CC) or raw recovered Carbon Black (raw rCB) is one of the immediate products of the pyrolysis process. This material has limited value and is primarily used for energy generation in cement kilns. Carbon Char, therefore, needs to be refined according to the market’s requirements and the final applications it will be used in, to be utilized as a technical product in high-value applications.
ASTM International – a standardization body that introduces key definitions of products and materials, with over 12,800 ASTM standards in development worldwide – recently published the first standard relating to recovered Carbon Black (rCB).
The ASTM Committee D36 on Recovered Carbon Black (rCB) was established in 2017 to support the emerging rCB industry in ensuring the quality and safety of their products. Several sub-committees are responsible for developing standards for terminology, guidance, practices, and testing methods.
The new ASTM standard (D8178) meets the need for a set of standard terms to clearly distinguish the value of rCB from Carbon Char (CC). Else, it facilitates the communication about the performance of rCB within proposed applications. D8178 outlines the importance of the differences between Char, Carbon Black (as defined by the ASTM Standard D3053), raw recovered Carbon Black, and recovered Carbon Black (rCB).
Most importantly, the product name “recovered Carbon Black” (rCB) should apply only if the raw Carbon Black is freed from metals and fibers and has been milled, which typically gives semi-reinforcing properties to rCB in rubber.
There are several processes to refine and add value to raw rCB (CC) according to the final product requirements. This can be limited to size screening and separation of foreign materials (such as metals and fibers) or using chemicals or other processes to remove specific components within the material. Refined carbon char derived from tire pyrolysis can be labeled as Recovered Carbon Black (rCB) and can be adapted for various processes for use in parts manufacturing. It can also be further refined for use by the chemical industry as a pigment and filler in inks, paints, and other materials.
Post-processing CC into rCB is complex and requires capital-intensive technologies. Refining this material further will significantly improve the properties of carbon char, remove a substantial proportion of foreign materials, and convert it into a high-value commodity that can replicate, to a reasonable degree, the properties of virgin black carbon. Depending on the application and performance requirements, rCB can replace between 10% and 100% of vCB in various manufacturing processes.
The holy grail application for recovered Carbon Black (rCB) is to be used by the tire manufacturing industry. The tire industry accounts for the majority of worldwide carbon black consumption. However, the tire industry is slow to replace higher contents of vCB with rCB or to accept large quantities in their production due to regulatory constraints, image concerns, and supply issues. But there is also a clear trend towards acceptance of rCB among tire manufacturers. Among others, Michelin has acquired a significant stake in a Swedish tire pyrolysis company and is planning an rCB production plant in South America.
Overview of uses of carbon black
Virgin carbon black has been used for decades as a reinforcing agent in tires and has become a key material for the entire rubber industry. Thanks to its unique properties, carbon black is used in the majority of tire and non-tire rubber industries. It has expanded to include pigmentation, ultraviolet (UV) stabilization, and conductive agents in a variety of everyday and specialty high-performance products. The international carbon black association (ICBA) classified the uses of carbon black as follows:
- Tires and Industrial Rubber Products: Carbon black is added to rubber as both a filler and a reinforcing agent. For various types of tires, it is used in inner liners, carcasses, sidewalls, and treads, utilizing different types based on specific performance requirements. Carbon black is also used in various molded and extruded industrial rubber products, including belts, hoses, gaskets, diaphragms, vibration isolation bushings, air springs, chassis bumpers, and multiple types of pads, boots, wiper blades, conveyor wheels, and grommets.
- Plastics: Carbon blacks are now widely used for conductive packaging, films, fibers, moldings, pipes and semi-conductive cable compounds in products such as refuse sacks, industrial bags, photographic containers, agriculture mulch film, stretch wrap, and thermoplastic molding applications for automotive, electrical/electronics, household appliances and blow-molded containers.
- Electrostatic Discharge (ESD) Compounds: Carbon blacks are carefully designed to transform electrical characteristics from insulating to conductive in products such as electronic packaging, safety applications, and automotive parts.
- High-Performance Coatings: Carbon blacks provide pigmentation, conductivity, and UV protection for various coating applications, including automotive (primer basecoats and clearcoats), marine, aerospace, decorative, wood, and industrial coatings.
- Toners and Printing Inks: Carbon blacks enhance formulations, delivering broad flexibility in meeting specific color requirements.
Although there are many uses for carbon black, different applications require different qualities and properties of carbon black.
The quality of carbon black depends on the process and the equipment. Therefore, while deciding on the equipment to buy, the desired quality of carbon black and the demand of these applications should be taken into consideration.
Market potential and major rCB demand drivers
Considering that rCB is a partial and complete replacement for vCB in various industries, the market potential for rCB is primarily determined by the current market for vCB. According to various industry experts and our estimates, the worldwide consumption of vCB has increased continuously over the last five years, with an estimated range of 11-13 million tons per year. This represents an annual total of nearly 16 billion EUR.
The most common use of vCB is in rubber and plastic applications due to its dual properties as both filler and reinforcing agent. Due to its ability to reinforce rubber, it is widely used in the tire manufacturing industry. In other rubber and plastic applications, it is used as filler. In this instance, filler serves as a diluting agent and is primarily used to reduce volume costs. These applications account for over 95% of total world CB consumption. Around 4% of CB is used as ink pigments due to its excellent tinting properties, and the remaining fraction is used in other applications.
Chart: Carbon black end-use Markets
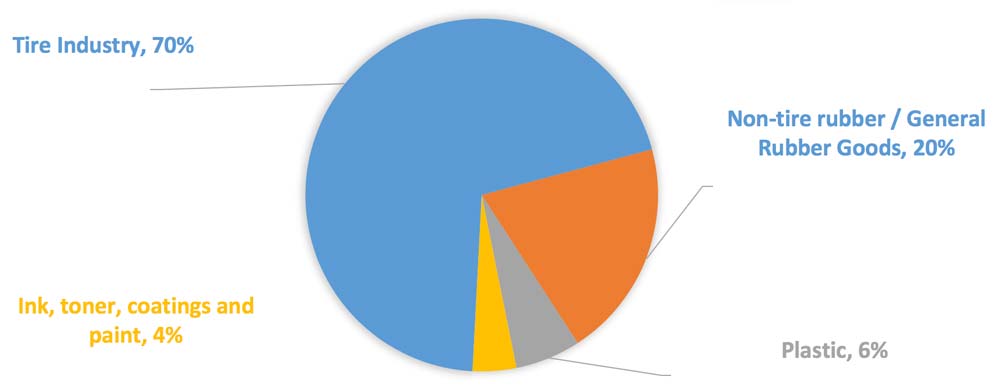
The tire industry remains the largest consumer of virgin carbon black, with overall consumption in the range of 9 million tons in recent years. It is characterized by a small number of large players that dominate the market and hold significant leverage with suppliers. The industry accounts for approximately 70% of the worldwide consumption of carbon black. Within this category, passenger tires account for 45% of the carbon black consumption, truck and bus tires account for 32%, and other tires (including OTR, motorcycle, and aircraft tires) account for 23%.
Non-tire rubber products represent the second biggest segment in carbon black consumption, 20% overall, close to 2-2.5 million tons per year. This includes all rubber applications aside from tires and retreads and is diversified mainly across several industries that manufacture products for rubber belts, wires, industrial rubber, and other sectors that employ carbon black in their compounding activities.
Plastics and inks can be categorized as specialty markets, representing approximately 10% of the vCB consumption at 1-1.2 million tons per year. This segment is also diversified across various end applications and different grades and custom-made CB formulations required to achieve specific performance. The use of vCB in this segment is primarily focused on serving as a pigment or performance filler.
Our research suggests that up to 100% of virgin carbon black can be replaced in specific applications, including plastic masterbatches, roofing products, and inks. In contrast, other applications have more modest replacement rates. For instance, 30%-50% of vCB could be replaced by rCB in passenger car tire sidewalls.
Assuming a substitution rate of 20%, we estimate that the annual volume of the global rCB market can account for some EUR 3.2 billion.
This makes the pyrolysis business focused on rCB production a profitable venture. While the success of the company depends on multiple factors, such as production technology and quality of output, there are vast market opportunities available for pyrolysis operators.
We see potential for the recovered carbon black in the global CB market. Still, we are also convinced that this growth is inevitable due to the persistent political shift in developed economies towards sustainable and environmentally friendly technologies. Today, newcomers to the market have a unique opportunity to shape the rCB industry and lead it in the following decades.
Concerted efforts needed to boost industry’s potential
Yet, to boost the use of recovered carbon black by the industry and accelerate the development of the rCB industry, concerted efforts from all stakeholders are needed. The rCB industry very much relies on regulations and research. The latter is needed to enable pyrolysis operators to create a more homogeneous and stable output, while the former would facilitate the industry’s inclusion in the circular economy loop.
The lack of standardization of rCB principally caused regulatory constraints in big industries. The good news is that ASTM is making progress in this matter and is developing specific standards for rCB. As typical carbon black characterization methods, based on structural level and surface area measurements, may not correlate with in-rubber performance equally for recovered Carbon Black products, ASTM will drive the identification of specific test methods for rCB. However, rCB is a sustainable product in terms of a circular economy and offers various benefits across different applications.
rCB Is the Future of Carbon-Based Manufacturing
With global pressure to reduce emissions and eliminate waste, recovered carbon black (rCB) provides manufacturers a cost-effective, low-carbon alternative to traditional carbon black without compromising performance.
Klean Industries Is Leading the rCB Revolution:
✅ Proven pyrolysis systems producing high-quality rCB
✅ ISCC-certified recovered materials ready for global markets
✅ Carbon upgrading systems for rubber, plastics & pigments
✅ KleanLoop™ traceability for supply chain transparency & ESG reporting
You can return to the main Market News page, or press the Back button on your browser.

